All Bank IFSC Code
Here We provide you to all Respective Bank IFSC Code….


Another way to Know the IFSC Code of Your Branch?
- RBI website
- Cheque leaf
- Passbook
- Official bank website
Where to Using IFSC Code
– Enables net banking or online banking operations
– Money transactions without error
– Instantaneous money transfers using NEFT and RTGS
– Quick and safe fund transfers
– Instantaneous Fund Transfer to Anywhere
– Cash transaction without paper
– Immediately validating payments
What is an IFSC Code ?
The acronym IFSC stands for “Indian Financial System Code.”The Reserve Bank of India has made the use of the standardized IFSC code convenient for locating specific bank branches. By retrieving any bank information, it is an 11-character long, one-of-a-kind alphanumeric code that speeds up online fund transfers. When they engage in different types of money transfer, such as NEFT, RTGS, IMPS, and UPI, this becomes crucial.
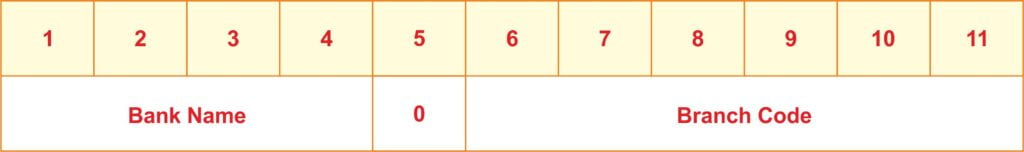

Complete Definition of an IFSC?
A bank’s name will be represented by the first four letters of an IFSC. Zero, or the fifth character, is used. Following these letters are six characters that typically signify the branch of the bank but might alternatively be digits or letters.


Banking System
The banking industry plays a crucial role in the economy by offering both businesses and consumers financial services. Banks provide a variety of financial services and products, including loanmaking and deposit taking. Governments control the banking industry to protect the stability of the financial system.
Regional rural banks, private sector banks, foreign banks, and public sector banks make up India’s banking industry. The banking industry has expanded quickly in recent years and is predicted to do so in the years to come.
With more than 100 scheduled commercial banks and more than 96,000 branches, India has one of the largest and most complicated banking sectors in the world. Public sector banks (PSBs), which make up over 70% of all banking assets, are the dominant players in the market. 20% of the total banking assets are held by private sector banks, with foreign banks holding the remaining 10%.
The banking industry in India has advanced significantly in recent years. It has improved in efficiency and focus on the needs of the consumer, and it has been essential in providing funds for the nation’s economic expansion. High levels of non-performing assets (NPAs) and the need for greater adoption of digital banking are two issues that the industry still has to deal with.
The Indian banking sector is well-positioned to play a key role in the country's economic growth in the years to come. The sector is expected to grow at a healthy pace in the coming years, and it is expected to contribute significantly to the country's GDP growth.


