Introduction
The Indian banking sector, a critical component of the country’s financial system, has witnessed dramatic developments over the years. With a rich history and a diverse banking landscape, it plays a critical role in promoting economic growth and financial stability in India. The purpose of this essay is to look into the evolution, current situation, difficulties, and future prospects of the Indian banking sector.
India’s Banking Evolution
Banking in India extends back to ancient times when merchants and moneylenders conducted financial transactions. The formal banking system began to emerge during the British colonial era, with the founding of the Bank of Bengal in 1806. Following that, the Bank of Bombay and the Bank of Madras were established.
Following independence in 1947, major banks were nationalized in 1969 and 1980. These changes intended to enhance the banking system and increase financial inclusion.
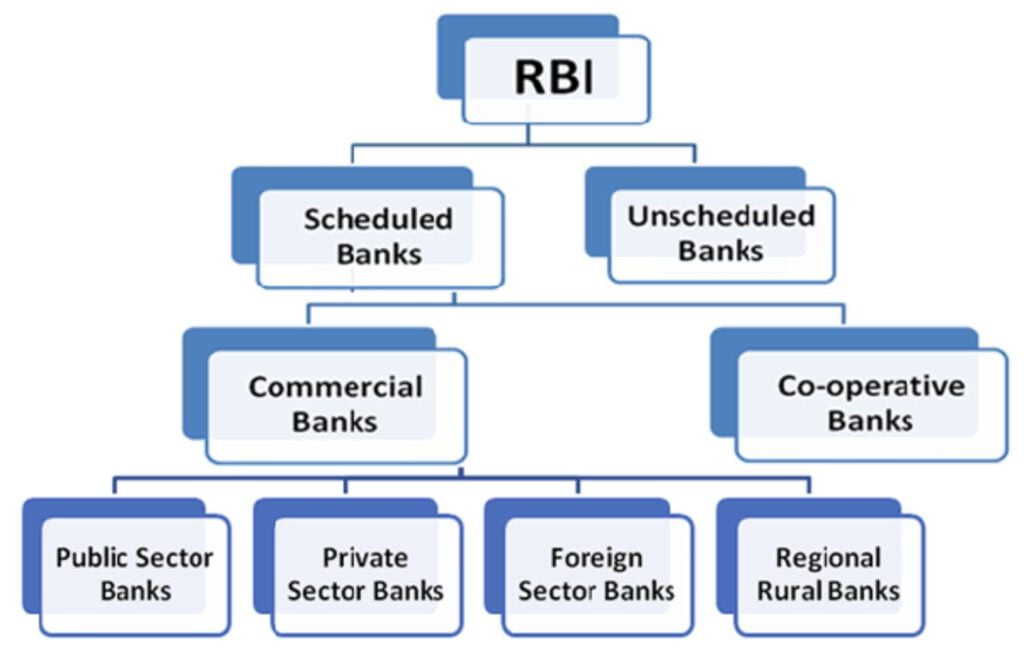

India’s Bank Types
The Indian banking sector is essentially divided into public sector banks, private sector banks, foreign banks, and cooperative banks. Public sector banks are owned by the government, and private sector banks are owned by private companies. Foreign banks have their headquarters in another country but operate in India, whereas cooperative banks are created by cooperative societies to provide banking services to their members.
The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) role
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) serves as the country’s central bank, regulating and supervising the banking sector. It develops and implements monetary policy, issues currency, and oversees the nation’s banking and financial sector.
Current Banking Trends in India
In recent years, the Indian banking sector has seen substantial changes, mostly due to technological advances. The digital revolution has resulted in the creation of FinTech companies that provide novel financial solutions, disrupting established banking procedures. Furthermore, the government’s financial inclusion measures, such as the Jan Dhan Yojana, have brought millions of unbanked residents into the official banking system.
Indian Banking Sector’s Challenges
Despite its expansion, the sector confronts various hurdles. Non-performing assets (NPAs) continue to be a source of concern for banks, harming their financial health. Maintaining enough capitalization and adhering to Basel rules are continuing issues. Furthermore, cybersecurity concerns pose a substantial threat, needing strong security measures.
Initiatives by the Government to Strengthen the Banking Sector
The government has taken several steps to strengthen the Indian banking sector. Bank recapitalization has been a critical step in strengthening their financial stability. Furthermore, bank mergers have tried to create stronger and more stable institutions. The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana has been significant in bringing the unbanked population into the fold of formal banking.
Prospects for the Future
The Indian banking industry has enormous growth potential. With a large and diverse consumer base, banks have the ability to broaden their reach and offer personalised financial products and services. The country’s ambitious infrastructure development plans and economic growth trajectory bolster the sector’s potential.
Technology’s Role in Banking
Technology has transformed the way banking services are delivered. Online banking platforms and smartphone applications have become the standard, allowing users convenient access to their accounts and other financial services. Furthermore, artificial intelligence and machine learning have improved banks’ operational efficiency and risk management skills.
Customer Support and Experience
Banks are increasingly focusing on improving the client experience. Individual demands are met through personalized banking services and specialized financial solutions. Improving customer service and effective grievance redressal processes have become critical for fostering consumer trust and loyalty.
Banking Rules and Regulations
As financial crime has increased, adherence to banking regulations and compliance measures has gotten more strict. KYC (Know Your Customer) standards and anti-money laundering (AML) safeguards are critical to the integrity of the financial system.
Financial Inclusion and Banking Institutionalization
Despite substantial progress, financial inclusion remains an issue in rural communities. Extending financial services to rural areas is critical to ensuring that every citizen has access to banking services. Initiatives like as the Jan Dhan Yojana have made significant gains in this area.
Future Challenges and Planning
The Indian Banking Sector must keep ahead of the curve as the world of finance advances at a rapid pace. Adapting to technology innovations and incorporating them into operations will be critical for banks to remain competitive. Additionally, monitoring and addressing the impact of global economic trends will be critical for successfully navigating uncertainty.
Conclusion
The journey of the Indian banking sector has been one of expansion, resilience, and transformation. It has grown from humble origins to become a vital factor in India’s economic development. However, it faces obstacles that necessitate ongoing adaptation and innovation. With a robust regulatory framework, significant government efforts, and technological breakthroughs, the sector is positioned for future growth and success.
FAQs
- What are the different kinds of banks in India?
- There are four types of banks in India: public sector banks, private sector banks, foreign banks, and cooperative banks.
- What role does the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) play?
- The RBI is India’s central bank, in charge of regulating and supervising the banking sector as well as establishing monetary policies.
- What are the most recent banking trends in India?
- Digitalization, the rise of FinTech companies, and government-led financial inclusion efforts are examples of recent trends.
- What are the issues that the Indian banking sector is facing?
- Non-performing assets (NPAs), capital sufficiency, and cybersecurity threats are among the challenges.
- What impact does technology have on the banking industry?
- With online platforms, smartphone apps, and the use of AI and machine learning for operational efficiency, technology has transformed banking.
