Overview of SWIFT Codes
SWIFT Codes are essential in the world of international banking and financial operations. Globally, certain banks and financial institutions are identified by these distinctive codes, facilitating efficient and secure communication during cross-border transfers. This article will examine what SWIFT Codes are, how they are organised, why they are significant, and other related topics.
A SWIFT Code: What Is It?
The term “Quick Code,” also known as “Bank Identifier Code” (BIC), refers to a fascinating, easily recognisable proof code used by financial institutions all over the world. It serves as an international standard for identifying banks and ensuring safe correspondence for various financial transactions. Each Quick Code consists of a mix of letters and numbers that express specific information about the bank and its region.
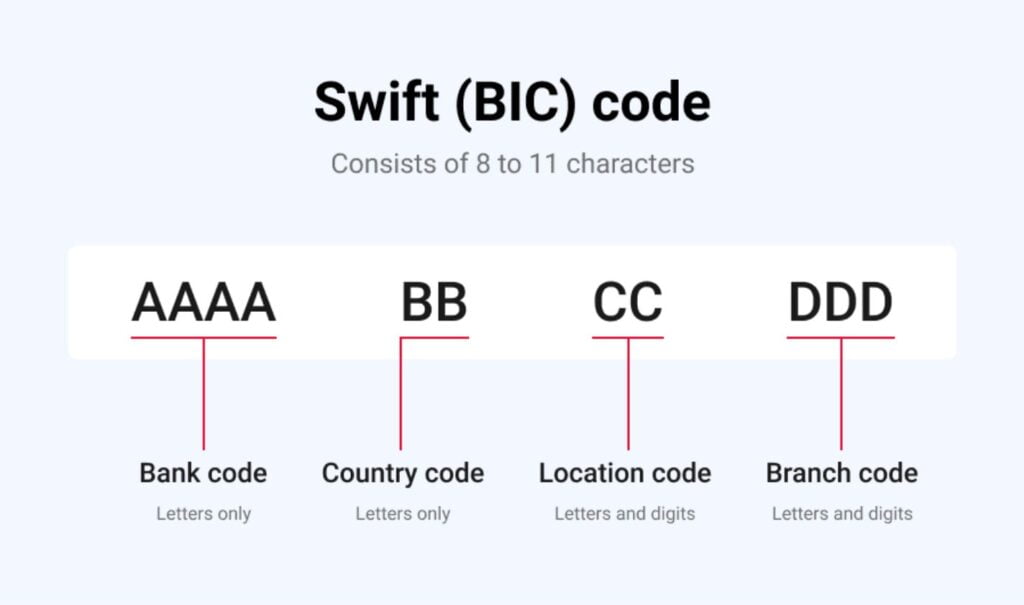

SWIFT Code’s Basic Structure
Either 8 or 11 characters make up a SWIFT Code in most cases. The name or code of the bank is revealed by the first four characters. The following two characters stand in for the nation where the bank is situated. The next two characters, typically in the form of a city code, specify the location of the bank. Finally, the optional three characters specify the bank’s branch code.
Take the SWIFT Code “ABCDUS3DXXX” as an illustration. In this case, “ABCD” denotes the bank code, “US” denotes the nation (United States), “3D” denotes the place (New York), and “XXX” denotes the branch code (optional).
SWIFT codes’ intended use
SWIFT Codes’ main objective is to provide standardised, secure communication between financial institutions all over the world. When processing international transactions like wire transfers, payments, and other financial activities, these identifiers allow banks to precisely identify one another. SWIFT Codes minimise the possibility of mistakes and delays by ensuring that funds are sent to the appropriate bank and branch.
How Can I Locate a SWIFT Code?
Thanks to several internet resources and tools, discovering a SWIFT Code is quite easy. By going to the bank’s or financial institution’s official website, one can learn the SWIFT Code. The majority of banks offer SWIFT Codes on their websites or have specific search capabilities to assist consumers in finding the right code.
As an alternative, there are a number of directories and databases available online that are made expressly for searching SWIFT Codes. Users of these websites can look up SWIFT Codes using criteria such as bank names, locations, or other pertinent information. Users can instantly retrieve the SWIFT Code they require by providing the necessary details.
SWIFT Codes’ Importance for Global Banking
For a number of reasons, SWIFT Codes are essential to global banking. First and foremost, they make sure that banks taking part in international transactions are accurately and securely identified. Due to similar bank names or locations, this helps avoid any mistake or inaccuracies that can arise.
Second, SWIFT Codes help international wire transfers to be processed efficiently. The SWIFT Code is used to send money to the right recipient bank when sending money from one nation to another. This guarantees that the money will be delivered securely and on time to the appropriate beneficiary.
Thirdly, SWIFT Codes allow banks to transmit crucial details about the source, final destination, and objective of international transactions. The global banking system needs this information to be transparent generally and to comply with regulations and fight money laundering.
Foreign wire transfers and SWIFT codes
International wire transfers are one of the most frequent uses of SWIFT Codes. The SWIFT Code of the beneficiary bank is necessary when a person or organisation starts a wire transfer from one nation to another. By using this code, you can be sure that your money will be delivered safely and precisely to the right account.
The SWIFT Code is used by the sending bank to determine the beneficiary’s bank throughout the wire transfer process. It makes it possible for the two banks to create a secure channel of communication and share crucial transaction information. Included in this data are the account numbers, account holders’ names, transfer amounts, and any special instructions.
The Benefits of SWIFT Codes
In the field of international banking, using SWIFT Codes has a number of benefits. The first benefit is that they improve the accuracy and speed of cross-border transactions by removing mistakes and misunderstandings that might happen when depending only on bank names or addresses.
Second, SWIFT Codes give financial organisations the ability to maintain an internationally standardised framework for transactions. This standardisation streamlines the procedure and lessens the complexity involved in locating and validating banks across various nations and areas.
Additionally, SWIFT Codes help to ensure the general security of global financial operations. These codes’ distinctive identity guarantees that money is sent to the right banks and reduces the possibility of fraud or misrouting.
Problems and Restrictions with SWIFT Codes
Although SWIFT Codes are widely used and are a vital tool in international banking, they are not without difficulties and restrictions. The potential for mistakes or delays in transactions brought on by inaccurate or out-of-date SWIFT Codes is one restriction. Before beginning any cross-border transactions, individuals and organisations must make sure the SWIFT Code is accurate.
The high cost of international wire transfers using SWIFT Codes presents another difficulty. Fees charged by financial institutions for executing these transactions can differ based on the amount being moved and the banks involved. These costs can occasionally add up, especially for little purchases.
SWIFT code substitutes
New systems and processes for doing international business are emerging as a result of technological advancements. Some of these substitutes try to overcome the SWIFT Codes’ drawbacks and provide quicker, more affordable options. One such instance is the use of blockchain technology, which offers enhanced transparency, efficiency, and cost savings, for international payments.
In order to make domestic and international transactions easier, certain nations and regions have also established localised payment systems. These programmes, like the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) in Europe, offer a standardised platform for transactions within the region, sometimes doing away with the requirement for SWIFT Codes.
SWIFT Codes’ Future
SWIFT Codes continue to be essential in international banking despite the difficulties and new alternatives. Financial institutions all across the world are aware of and use the SWIFT network, ensuring interoperability and secure communication. The importance and purpose of SWIFT Codes could change in the future, though, as technology develops and new solutions are created.
Conclusion
Finally, SWIFT Codes are crucial resources in the field of international banking. They offer a standardised and safe way to identify banks and make cross-border transactions easier. SWIFT Codes enable precision, quickness, and openness in the world’s financial system because to their distinctive structure and ubiquitous use.
FAQs
What exactly does SWIFT mean?
For all interbank financial media transmissions, Quick speaks for the general public.
IBAN numbers and SWIFT codes are same, right?
No, IBAN numbers and SWIFT codes have different uses. IBAN numbers identify particular bank accounts, whereas SWIFT codes identify banks.
Can I transact with a specific bank using the same SWIFT Code every time?
Most of the time, sure. The SWIFT Code of a bank normally applies to all of its branches, although for some transactions it is wise to double check the SWIFT Code with the particular branch.
SWIFT Codes are they private?
No, SWIFT Codes are accessible to the general public and can be found online or by contacting the relevant banks.
Is a SWIFT Code permissible for domestic transactions?
International transactions are where SWIFT Codes are most frequently utilised. Routing numbers or regional payment systems are frequently used for domestic transfers.
